Dedicated server
Hosting a Project Zomboid dedicated server can be done in Windows or Linux.
Downloading the Server Files
Through Steam
- Navigate to your Steam library and filter for tools
- Locate 'Project Zomboid Dedicated Server' and download/install it
Note: Do not launch the server via Steam. If accidentally done, verify the integrity of the files.
Through SteamCMD
SteamCMD is the command line version of Steam. The Valve Developer wiki has instructions on how to download and configure SteamCMD.
Windows
Once you have downloaded and extracted SteamCMD to the folder of your choosing, run it by executing steamcmd.exe from a command line.
You can now set up the installation directory where the dedicated server files will be stored.
The following is an example of setting the download directory to its own separate folder on the C: drive. You can choose wherever you would like to store the server files.
force_install_dir C:\PZServer
For Linux users, the server will install to /home/<MYOURUSERNAME>/.steam/steam/steamapps/common/Project Zomboid Dedicated Server/ unless specified otherwise.
Once you have set the install directory to your preference, login anonymously to Steam:
login anonymous
Next, download the Project Zomboid dedicated server files:
app_update 380870 validate
Once you see the message "Success! App '380870' fully installed", close SteamCMD:
quit
Linux
For Debian and Ubuntu, first install steamcmd
Some of these commands may need to be run as root. To gain root access, you likely use "sudo" to elevate permissions on your system.
For example:
- This command assumes you are root dpkg --add-architecture i386 - So you may need this instead: sudo dpkg --add-architecture i386
If you cannot find the package `steamcmd`, you might need to enable `non-free` repository
apt-get install software-properties-common -y apt-add-repository non-free
Proceed to Install `steamcmd`
dpkg --add-architecture i386 apt-get update apt-get install steamcmd
Don't run the server as root. Add an user such as pzuser
adduser --disabled-password pzuser
We will install Zomboid Server in /opt/pzserver
mkdir /opt/pzserver chown pzuser:pzuser /opt/pzserver
Log in as pzuser
su - pzuser
If you use "sudo" to handle privilege escalation, use
sudo su - pzuser
Create the configuration file /home/pzuser/update_zomboid.txt that will manage steamcmd
cat >$HOME/update_zomboid.txt <<'EOL' // update_zomboid.txt // @ShutdownOnFailedCommand 1 //set to 0 if updating multiple servers at once @NoPromptForPassword 1 force_install_dir /opt/pzserver/ //for servers which don't need a login login anonymous app_update 380870 validate quit EOL
Now install Project Zomboid Server. You will use this same command every time you want to update the server to the latest version.
steamcmd +runscript $HOME/update_zomboid.txt
Forwarding Required Ports
Project Zomboid dedicated servers require the following open ports to successfully connect to clients:
16261 UDP
16262 UDP - Direct Connection Port
Running Multiple Servers from a Single Box
The ports above are default for the first server in the "SERVERNAME.ini" file. If you're running multiple instances of PZ on a single Linux Box, you'll need to follow these steps:
- Create 2 separate accounts in Linux from the home directory
- Run steamcmd in under both users to create two instances of steamcmd.
- Run the <login anonymous> & <app_update 380870 validate> commands under both users (via scripts if preferred - you'll need to duplicate the scripts above under each user and edit directories accordingly if so)
- Before running the 2nd server instance, be sure to open further UDP ports on your Server (e.g. 16274 + 16275).
- Edit the "SERVERNAME.ini" file in the 2nd Steam Instance to reflect these ports under the UDP Port settings).
Each instance will require 2 clear UDP ports.
Ports used before version 41.77
16261 UDP
8766, 8767 UDP
Running the Server
Windows
Navigate to the download folder you specified (C:\pzserver if you followed the above steps) and locate the three StartServer batch files.
The default download directory if you used Steam to install the server is C:\Program Files (x86)\Steam\steamapps\common\Project Zomboid Dedicated Server
Run the batch file that corresponds with your operating system. For most use cases this will be 64-bit unless you are intentionally running 32-bit or running the non-Steam version.
Important note: By default the StartServer64 batch file specifies 16GB of starting memory for the server. You must edit the StartServer64 file and change the -Xms and -Xmx files to the values you want to use for server memory, or the server will fail to start with memory errors.
An example with 6GB used for the amount of memory (note the -Xms and -Xmx values):
".\jre64\bin\java.exe" -Djava.awt.headless=true -Dzomboid.steam=1 -Dzomboid.znetlog=1 -XX:+UseZGC -XX:-CreateCoredumpOnCrash -XX:-OmitStackTraceInFastThrow -Xms6g -Xmx6g -Djava.library.path=natives/;natives/win64/;. -cp %PZ_CLASSPATH% zombie.network.GameServer -statistic 0
For reference, this is equivalent to the "Server Memory" option when using "Host" from the main menu to host a local multiplayer server.
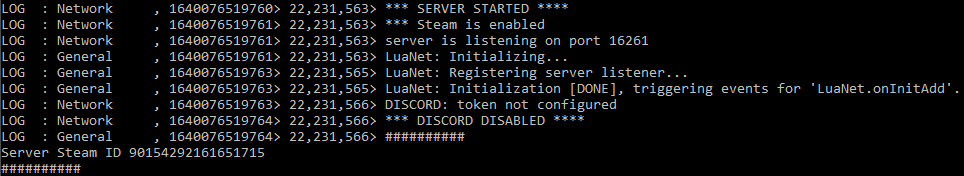
Launching a server will open a command console window that begins executing the server on your machine. On the first run, it will prompt you to set a password for the admin account it will create. After the server finishes setting up with default game settings, a message will output indicating success or failure.
Linux
Navigate to your installation folder (default: /home/YOURUSERNAME/.steam/steam/steamapps/common/Project Zomboid Dedicated Server) and start the start-server.sh file. The following example uses the default folder:
cd ~/.steam/steam/steamapps/common/Project\ Zomboid\ Dedicated\ Server\/
Then start the start-server.sh
bash start-server.sh
However, if you followed the instructions in this page to install Project Zomboid Server via steamcmd in Linux, you just need to execute the following command:
/opt/pzserver/start-server.sh
Optionally, you can change the name of the server, this will change which .ini file is used and it will create a new save folder by this new server name:
bash start-server.sh -servername SERVERNAME
Launching a server will open a command console window that begins executing the server on your machine. On the first run, it will prompt you to set a password for the admin account it will create. After the server finishes setting up with default game settings, a message will output indicating success or failure.
System.d
[WARNING], The Zomboid Devs explicitly discourage this method, the safeties currently in place should insure a proper saving sequence on server shutdown, but there are no guarantees. An option is to configure the server to run under system.d.
Before you do this:
- manually start the server (as described above) at least once because the first time you are asked to input an admin password
- make sure you are no longer logged in as pzuser (type exit if you are) - the system.d commands are to be run as root.
First, configure the system.d unit
cat >/usr/lib/systemd/system/zomboid.service <<'EOL' [Unit] Description=Project Zomboid Server After=network.target [Service] PrivateTmp=true Type=simple User=pzuser WorkingDirectory=/opt/pzserver/ ExecStart=/bin/sh -c "exec /opt/pzserver/start-server.sh </opt/pzserver/zomboid.control" ExecStop=/bin/sh -c "echo save > /opt/pzserver/zomboid.control; sleep 15; echo quit > /opt/pzserver/zomboid.control" Sockets=zomboid.socket KillSignal=SIGCONT [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target EOL
Second, add a "zomboid.socket FIFO service", this will allow us to issue commands to the server, and guarantee a safe shutdown.
cat >/usr/lib/systemd/system/zomboid.socket <<'EOL' [Unit] BindsTo=zomboid.service [Socket] ListenFIFO=/opt/pzserver/zomboid.control FileDescriptorName=control RemoveOnStop=true SocketMode=0660 SocketUser=pzuser EOL
Once you have done that, you have the following commands available:
# start a server systemctl start zomboid.service # stop a server systemctl stop zomboid.service # restart a server systemctl restart zomboid.service # check server status (ctrl-c to exit) systemctl status zomboid.service
The logs are now managed by journalctl. To access to the logs of the server, execute the following command:
journalctl -u zomboid.service -f
If you run into an issue where "zomboid.control" is not found, your socket may not have been initalized correctly. Try
systemctl start zomboid.socket
and then try again.
systemctl start zomboid.service
To send commands to the server, use the following command:
echo "command" > /opt/pzserver/zomboid.control
If you use sudo to elevate permissions on your system, you should use
sudo echo "command" | sudo tee /opt/pzserver/zomboid.control
To see if your command worked, check journalctl, a good command to test with is "help".
Connecting to the Server
- Launch Project Zomboid
- Click the Join menu option
- Click the Favorites tab
- Add your public IPv4 address
- Enter port (default: 16261)
- Input your account details (anything desired)
- Click Save, select the added server and join
Note I: Hosting a non-Steam dedicated server requires players connect through the non-Steam version of the game client. For Steam game owners, this can be achieved by adding '-nosteam' to the launch options of Project Zomboid under its properties menu.
Note II: If hosting a server for LAN or VPN clients, the local IPv4 address or VPN defined address needs to be used.
Note III: As of game version 41.65, players who host and play on the same machine can solely use the public IPv4 address to connect to their server. If connection issues are encountered, consider adding your local IPv4 address to the Local IP field on the server screen. This address can be determined by clicking Start on the desktop, typing cmd, hitting enter, typing ipconfig in the opened command prompt and hitting enter.
Administrating the Server
There are a myriad of tools available for server administrators to customize and manage their servers.
Configuring the Server Game Settings
Windows
Server Data Save Locations
By default the server will look for game settings and world data named servertest inside C:\Users\YourUsername\Zomboid. If this data does not exist, the server will generate it automatically using default game settings. Use the following table for reference.
| Filename | File Location | Description |
|---|---|---|
| servertest.ini | C:\Users\YourUsername\Zomboid\Server | This file contains the server configuration settings. Editable with notepad. |
| servertest_SandboxVars.lua | C:\Users\YourUsername\Zomboid\Server | This file contains the server sandbox configuration settings. Editable with notepad. |
| servertest_spawnpoints.lua | C:\Users\YourUsername\Zomboid\Server | This file contains the spawnpoints available in your server. Setting custom spawn points is possible. Editable with notepad. |
| servertest_spawnregions.lua | C:\Users\YourUsername\Zomboid\Server | This file contains the regions available for spawning (i.e. Muldraugh, Rosewood, etc). Editable with notepad. |
| n/a | C:\Users\YourUsername\Zomboid\Saves\Multiplayer\servertest | This folder contains the generated/saved world data of the server. |
Customizing Settings
Customizing server settings can be accomplished in two ways.
- Through the game client
- Editing the relevant files in notepad
To customize settings using the game client, launch Project Zomboid and select the Host menu option followed by the Manage Settings menu option.
If the server was successfully run at least once:
- Select servertest from the the list of saved server settings
- Click Edit Settings
- Edit desired settings and save
If the server was not run at least once:
- Click Create New Settings
- Name these settings servertest
- Edit desired settings and save
The next time the server successfully starts it will use the defined servertest.ini and lua files. The settings can be verified by using the admin command showoptions or opening servertest.ini, servertest_SandboxVars.lua, servertest_spawnpoints.lua, and servertest_spawnregions.lua in notepad.
Note: Changes can be saved to servertest.ini while the server is running. After servertest.ini is saved, use admin command reloadoptions to make the changes live.
Customizing Server Name
You may customize your server's name to something other than servertest in order to either have worlds you can quickly read and identify, or to be able to switch to a new world without having to move a bunch of files on both server and client side to preserve that world.
First and foremost, be aware that player map data is stored locally client side under your IP address and port. If you don't want map information bleedover, you may need to change the port in your server settings. If you are trying to save an existing server, you have two choices ahead of you. 1) never use port 16261 for any other PZ servers, or 2) have anyone who has previously joined look for a file named something like 123.45.0.12_16261_a589371111b0ccerf81acc30e918f8c9 [server ip address _ server port _ something] located at C:\Users\%your username%\Zomboid\Saves and have them put it somewhere safe or edit the folder name.
Next,
Make a copy of whichever one you use to launch servertest normally by selecting it, right clicking, select copy, right click somewhere in empty space, paste.
Rename the new file (or don't)
Open the file in some text editor (such as notepad) and insert -servername YOURSERVERNAME behind -cp %PZ_CLASSPATH% zombie.network.GameServer
Example with server name of "pizza":
@setlocal enableextensions @cd /d "%~dp0" SET PZ_CLASSPATH=java/istack-commons-runtime.jar;java/jassimp.jar;java/javacord-2.0.17-shaded.jar;java/javax.activation-api.jar;java/jaxb-api.jar;java/jaxb-runtime.jar;java/lwjgl.jar;java/lwjgl-natives-windows.jar;java/lwjgl-glfw.jar;java/lwjgl-glfw-natives-windows.jar;java/lwjgl-jemalloc.jar;java/lwjgl-jemalloc-natives-windows.jar;java/lwjgl-opengl.jar;java/lwjgl-opengl-natives-windows.jar;java/lwjgl_util.jar;java/sqlite-jdbc-3.27.2.1.jar;java/trove-3.0.3.jar;java/uncommons-maths-1.2.3.jar;java/ ".\jre64\bin\java.exe" -Djava.awt.headless=true -Dzomboid.steam=1 -Dzomboid.znetlog=1 -XX:+UseZGC -XX:-CreateCoredumpOnCrash -XX:-OmitStackTraceInFastThrow -Xms4g -Xmx4g -Djava.library.path=natives/;natives/win64/;. -cp %PZ_CLASSPATH% zombie.network.GameServer -servername pizza -statistic 0 PAUSE
Just running this will create a world with all the requisite files with the default settings which you can edit later. If you've already created a server with a name you want to use with all the settings set the way you want, use the same name as the file at C:\Users\%your username%\Zomboid\db
Linux
Server Data Save Locations
By default the server will look for game settings and world data named servertest inside ~/Zomboid (assuming you followed the instructions above that would be /home/pzuser/Zomboid. If this data does not exist, the server will generate it automatically using default game settings. Use the following table for reference.
| Filename | File Location | Description |
|---|---|---|
| servertest.ini | ~/Zomboid/Server | This file contains the server configuration settings. |
| servertest_SandboxVars.lua | ~/Zomboid/Server | This file contains the server sandbox configuration settings. |
| servertest_spawnpoints.lua | ~/Zomboid/Server | This file contains the spawnpoints available in your server. Setting custom spawn points is possible. |
| servertest_spawnregions.lua | ~/Zomboid/Server | This file contains the regions available for spawning (i.e. Muldraugh, Rosewood, etc). |
| n/a | ~/Zomboid/Saves/Multiplayer/servertest | This folder contains the generated/saved world data of the server. |
Admin Commands
The following commands can be executed either on the server console window or in-game (preceded by a forward slash when used in-game) provided the user has admin status. Some things are case sensitive (ex: Base.Axe works, but not base.axe)
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| addalltowhitelist | Add all the current users who are connected with a password to the whitelist, so their account is protected. |
| additem | Give an item to a player. If no username is given then you will receive item. Count is optional. Use: /additem \"username\" \"module.item\" count, ex : additem rj Base.Axe 1 |
| adduser | Use this command to add a new user to a whitelisted server. Use: /adduser \"username\" \"pwd\" ex: adduser rj 12345 |
| addusertowhitelist | Add a user connected with a password to the whitelist, so their account is protected. Use: /addusertowhitelist \"username\" ex: addusertowhitelist rj |
| addvehicle | Spawn a vehicle. Use: /addvehicle \"script\" \"user or x,y,z\", ex: addvehicle Base.VanAmbulance rj |
| addxp | Give experience points to a player. Use: /addxp \"playername\" perkname=xp, ex: addxp rj Woodwork=2 |
| alarm | Sound a building alarm at the Admin's position. (Must be in a room.) |
| banid | Ban a SteamID. Use: banid SteamID |
| banuser | Ban a user. Add a -ip to also ban the IP. Add a -r \"reason\" to specify a reason for the ban. Use: /banuser \"username\" -ip -r \"reason\". For example: banuser rj -ip -r spawn kill |
| changeoption | Change a server option. Use: /changeoption optionName \"newValue\" ex: changeoption SleepAllowed true |
| chopper | Place a helicopter event on a random player |
| createhorde | Spawn a horde near a player. Use : /createhorde count \"username\", ex: createhorde 150 rj, username is optional except from the server console. |
| createhorde2 | Unknown (ERROR: Missing translation "UI_ServerOptionDesc_CreateHorde2") |
| godmode | Make a player invincible. No username set will toggle self-invincibility. Use: /godmode \"username\" -value, ex godmode rj -true (could be -false) |
| gunshot | Place gunshot sounds on a random player |
| help | Outputs a list and description of admin commands |
| invisible | Make a player invisible to zombies. No username provided will toggle invisibility on yourself. Use: /invisible \"username\" -value, ex: invisible rj -true (could be -false). |
| kickuser | Kick a user. Add a -r \"reason\" to specify a reason for the kick. Use: /kickuser \"username\" -r \"reason\" |
| noclip | Makes a player pass through walls and structures. Toggles with no value. Use: /noclip \"username\" -value, ex: noclip rj -true (could be -false) |
| players | List all connected players |
| quit | Save and shut down the server |
| releasesafehouse | Release a safehouse you own. Use: /safehouse release |
| reloadlua | Reload a Lua script. Use: /reloadlua \"filename\" |
| reloadoptions | Reload server options (servertest.ini) and send to the clients. Useful for implementing game setting changes while players are connected. |
| removeuserfromwhitelist | Remove a user from the whitelist. Use: /removeuserfromwhitelist \"username\" |
| removezombies | Command name self-explanatory, but have not tested. (ERROR: Missing translation "UI_ServerOptionDesc_RemoveZombies") |
| replay | Record and play replay for moving player. Use: /replay \"playername\" -record\-play\-stop \filename.\ Example: /replay user1 -record test.bin |
| save | Saves the current game world |
| sendpulse | Toggle sending server performance info to this client. Use: /sendpulse |
| servermsg | Broadcast a message to all connected players. Use: /servermsg \"text\" |
| setaccesslevel | Set access level of a player. Current levels: admin, moderator, overseer, gm, observer. E.g. setaccesslevel userName admin / Note: To remove any access level, use "none" in place of admin. |
| showoptions | Show the list of current server options and values. |
| startrain | Start rain on the server |
| stoprain | Stop rain on the server |
| teleport | Teleport to a player. Use: /teleport \"playername\" or /teleport \"player1\" \"player2\", ex /teleport \"rj\" or /teleport \"rj\" \"toUser\" |
| teleportto | Teleport to coordinates. Use: /teleportto x,y,z, ex /teleportto 100098,189980,0 |
| unbanid | Unban a SteamID. Use: /unbanid SteamID |
| unbanuser | Unban a player. Use : /unbanuser \"username\" |
| voiceban | Block voice from user \"username\". Use : /voiceban \"username\" -value, ex /voiceban \"rj\" -true (could be -false) |